

Infertility Treatment Singapore
If you are having trouble getting pregnant, be comforted that you are not alone – about 15% of couples struggle with infertility. Seeing a gynaecologist for a fertility investigation can help you find the cause of infertility and allow you to receive a fertility treatment that is tailored to your needs.
Infertility is defined as the inability of a couple to become pregnant despite having regular and unprotected intercourse after a year. However, if If you are over 35 years old and have been unsuccessful at conceiving after trying for 6 months, you are highly encouraged to seek fertility treatment as the risks of genetic disorders, miscarriage and infertility also increase with age.
Testing may involve:
- Thorough review of medical history
- Physical examination
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
- Ultrasound scan
- Ovulation evaluation
- Semen analysis
- Hysteroscopy to look inside the uterus. During this procedure, samples of the endometrium may be taken to study.
- Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure used to inspect the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and the outside of the uterus. Your doctor may assess the tubes to see if they are patent or blocked. During a laparoscopy, any ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis and pelvic adhesions found can be treated as well.
Depending on the test results, treatments like removing abnormal growths, ovulation induction, and assisted reproductive technology (ART) techniques may be recommended. This includes intrauterine insemination (IUI), in which sperm is injected directly into the uterus, and in vitro fertilization (IVF), where fertilization occurs outside the body.
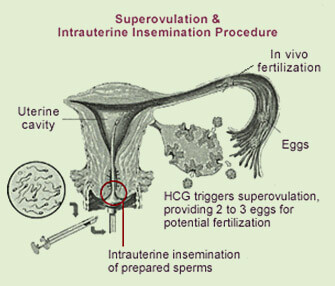
Superovulation and Intrauterine Insemination (SO-IUI)
- Both fallopian tubes must be patent in order for SO-IUI to be performed. Couples with mild endometriosis, mild male factor infertility, cervical abnormalities or unexplained infertility can undergo the procedure.
- Oral clomiphene citrate or gonadotropin (GnRH) injections are given to stimulate the ovaries to produce several mature follicles (eggs) at the same time. An ultrasound is regularly performed to detect the number and size of the eggs in the ovaries.
-
On insemination day, a fresh sample of the man’s semen is brought to the lab. The semen is then processed and placed directly into the womb through a fine tube. Medications are given to help facilitate implantation and pregnancy. A simple pregnancy test is performed 14 - 17 days following the insemination.
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
- In-vitro fertilization (IVF) uses sperm to fertilize eggs from the woman in a lab. This is offered to women with blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, severe endometriosis, ovulatory problems, unexplained infertility and severe sperm disorders.
-
High-dose gonadotropin (GnRH) injections are given to stimulate several follicles (eggs) to grow, and their maturation progress is monitored with serial ultrasound scans. When these follicles are sufficiently developed, they are removed from the ovaries.
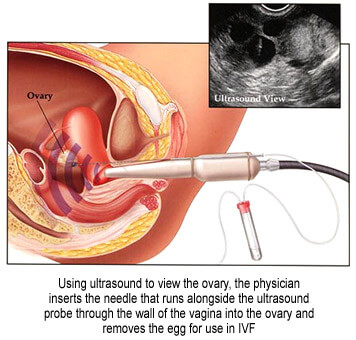
- Under direct ultrasound guidance, a needle is inserted through the vagina and into the ovary to retrieve the follicles. These eggs are then combined with healthy sperm in the lab to see if they become fertilized.
-
Similar to IVF, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) involves fertilizing eggs in a lab. The difference is that with ICSI, only one sperm is injected directly into a viable egg to help facilitate a successful fertilization. This may be a good option if sperm quality is very low. ICSI can be performed alone or in combination with IVF.
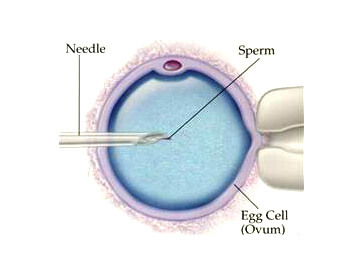
ICSI
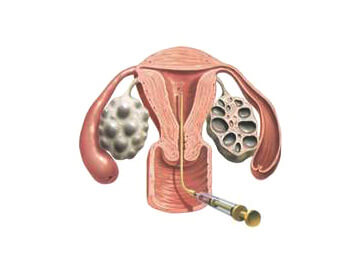
Embryo Transfer
- A few days later, one or two fertilized eggs (embryos) are placed into the woman’s uterus through the vagina. Any extra embryos that are not used may be kept frozen for later use.
- Hormonal support is recommended to increase the chances of implantation and pregnancy. After 14 – 17 days following embryo transfer, a successful IVF can be confirmed through a pregnancy test.
- Women’s Health Screening
- Infertility Management
- Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Urogynaecology
Click On Each Service To Read More

Website maintained by Activa Media. All rights reserved.
321 Clementi (WE Cinema Mall) Block 321 #01-05, Clementi Ave 3 Singapore 129905
Phone:+65 6873 3383
(Consultation by appointment only. No walk-ins)
Fax:+65 6873 3373
Emergencies Only:+65 6535 8833
(For appointments, please call clinic)
Email:gynaemdclementi@singnet.com.sg
Clinic Operating Hours:
Monday to Friday : 9am – 1pm, 2pm – 7pm
Saturday : 8:30am – 12:30pm
Closed on Sunday & Public Holidays
Website maintained by Activa Media. All rights reserved.